Filters meeting the HEPA standard must satisfy certain levels of efficiency. Common standards require that a HEPA air filter must remove—from the air that passes through—at least 99.95% (European Standard)[4] or 99.97% (ASME, US DOE) of particles whose diameter is equal to 0.3 μm; with the filtration efficiency increasing for particle diameters both less than and greater than 0.3 μm.
HEPA was commercialized in the 1950s, and the original term became a registered trademark and later a generic term for highly efficient filters. HEPA filters are used in applications that require contamination control, such as the manufacturing of disk drives, medical devices, semiconductors, nuclear, food and pharmaceutical products, as well as in hospitals, homes and vehicles.
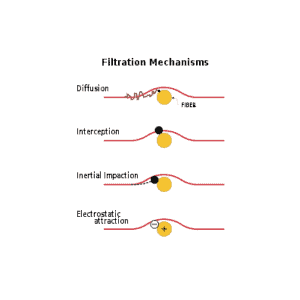
The four primary filter collection mechanisms: Diffusion interception, inertial impaction, and electrostatic attraction
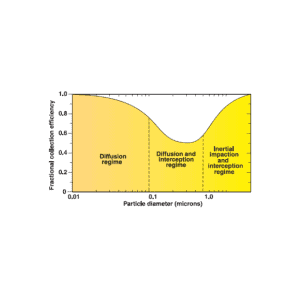
Classic Collection Efficiency Curve with Filter Collection Mechanisms